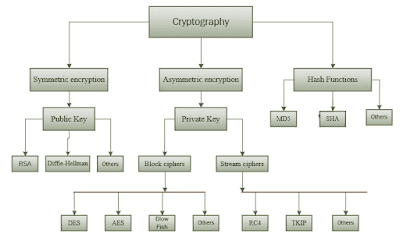
Cryptography:-
We can divided all the cryptography algorithms(ciphers) into three groups:
- Symmetric cryptography
- Asymmetric cryptography
- Hash Function
Symmetric cryptography:-
In symmetric-key cryptography, the same key is used by both parties. The sender uses this
key and an encryption algorithm to encrypt data; the receiver uses the same key and the
corresponding decryption algorithm to decrypt the data.
A symmetric encryption scheme has five ingredients:
• Plaintext: This is the original intelligible message or data that is fed into the algorithm as input.
• Encryption algorithm: The encryption algorithm performs various substitutions and transformations on the plaintext.
• Secret key: The secret key is also input to the encryption algorithm. The key is a value independent of the plaintext and of the algorithm.
• Ciphertext: This is the scrambled message produced as output. It depends on the plaintext and the secret key. For a given message, two different keys will produce two different ciphertexts. The ciphertext is an apparently random stream of data and, as it stands, is unintelligible.
• Decryption algorithm: This is essentially the encryption algorithm run in reverse. It takes the ciphertext and the secret key and produces the original plaintext.
Private key Cryptography:-
Symmetric encryption also called private-key encryption or secret-key encryption involves using the same key for encryption and decryption.





1 Comments
mam difference between single key and two key btha dy
ReplyDelete